
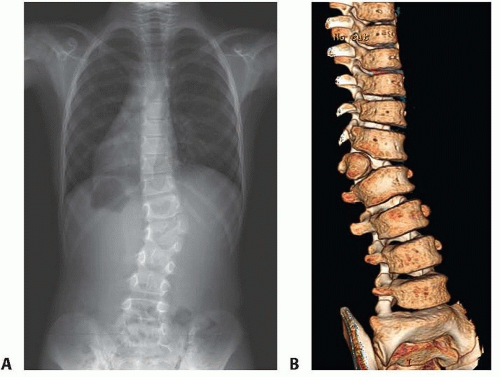
Choosing fusion levels on similar principles akin to AIS leads to avoidance of hemivertebra excision in most case including lumbosacral hemivertebra cases. This approach is safer compared to hemivertebra excision and has similar or better curve correction than previously reported. The radiographic and perioperative outcomes were similar to AIS patients. Conclusion: Patients with hemivertebra can benefit from hemivertebra sparing approach. The only significant difference was that hemivertebra patients had longer hospital stay (p = 0.001). Surgical time (p = 0.413) and blood loss (p = 0.954) were similar between the groups. Patients had a similar number of levels fused (p = 0.227) and a similar number of fixation points (p = 0.23). Plain radiograph / CT Usually directly outlines the bony anomaly and is often seen as a wedge-shaped vertebral body. Postoperative Cobb (1.0) and overall correction (p = 0.966) were similar. Radiographic features Antenatal ultrasound A hemivertebra may be seen as an asymmetrical vertebral body on sagittal or coronal scanning, while on axial scanning, a focal defect may be seen on either side of the vertebral column 5. Estimated blood loss was similar (p = 0.095) while surgical time (p 0.05). Postoperative Cobb (p = 0.048) was significantly larger for AIS patients (p = 0.048), however, overall Cobb correction was similar between the groups (% correction ) (p = 0.297). Results: When comparing hemivertebra to the most recent AIS patients, age (p = 0.81), BMI (p = 0.24) and preoperative Cobb (p = 0.06) were similar. Overall, 12 pairs (24 patients) were matched and analyzed to compare the surgeries after accounting for possible confounding variables. While performing a radiographic search for a study on congenital scoliosis in patients with congenital heart disease, an 11-month-old boy who was treated surgically for congenital heart disease in 1997 was found to have a sacral hemivertebra with no thoracic or lumbar. Patients were matched based on gender, age, BMI, and preoperative Cobb. Hemivertebrae are most commonly seen in the thoracic and lumbar regions but sacral hemivertebrae are very rarely seen. An additional rigorous analysis was done to match hemivertebra patients from a database of 330 AIS patients. These 24 patients were compared with the most recent 54 AIS correction surgeries with 2-year follow up. Methods: 24 patients with congenital scoliosis and associated hemivertebra were included. Our hypothesis is that this approach leads to similar perioperative correction and radiographic outcomes to AIS patients. The fusion levels are determined similar to AIS, as most of these patients have presented at a later age (>10 years) and have a deformity that extends over multiple segments. We have utilized a hemivertebra-sparing approach in these patients alongside multi-level Ponte osteotomies and all pedicle screw constructs for the past many years. It is however a technically challenging procedure and complications can include spinal cord injury, nerve root injury and CSF leak. Genetic aspects of early childhood scoliosis.Background: Hemivertebra excision in patients with congenital scoliosis is believed to give the best possible correction of congenital scoliosis while decreasing the number of levels fused. Connor JM, Conner AN, Connor RAC, Tolmie JL, Yeung B, Goudie D. Introduction Congenital scoliosis is the failure of normal vertebral development during 4th to 6th week of gestation caused by developmental defect in the formation of the mesenchymal anlage Epidemiology incidence prevalence in general population estimatedĭescriptive epidemiology of hemivertebrae, Hawaii, 1986–2002. live births 2.ĭescriptive epidemiology of hemivertebrae, Hawaii, 1986–2002.
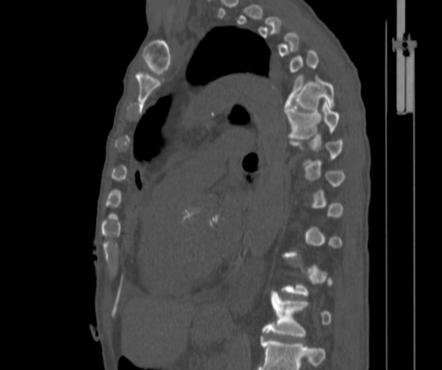
see cervical hemivertebra Epidemiology The estimated incidence is at ~0. Other types of hemivertebra, especially those involving unbalanced congenital scoliosis, usually progress markedly with growth and have a relatively poor prognosis unless early spinal fusion prevents further spinal curvature.Ī cervical location is rare and even rarer as a cause of cervical subluxation in flexion and extension (for which only one previous case has been found). In view of the poor prognosis of surgical intervention he was fitted with an Jewett brace so that further neurological impairment was avoided. Hemivertebrae, which are the most frequent cause of congenital scoliosis, pose a challenge in terms of prognosis and therapy. The strongest negative impact is when a hemivertebra occurs at the lumbo-sacral level 7. Prognosis The prognosis can be variable dependant on the type from being a progressive to non progressive deformity. The strongest negative impact is when a hemivertebra occurs at the lumbosacral level 7. Treatment and prognosis The prognosis can be variable dependent on the type of segmentation anomaly, from being a progressive to a non-progressive deformity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
